Short-wave infrared (SWIR) sensors are becoming significantly important in various industries, especially additive manufacturing. These sensors provide unique capabilities that enable processes such as defect detection, real-time monitoring, and control over specific properties. In this blog post, we discuss how SWIR sensors are used in additive manufacturing and the benefits they provide.
What are SWIR Imaging Sensors?
SWIR sensors operate in the short-wave infrared spectrum, a wavelength range between the visible light and the long-wave infrared. These sensors utilize materials like Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs) to capture and detect SWIR wavelengths, which is necessary to visualize objects or processes that may be invisible to the naked eye. With their ability to detect radiation in this range, SWIR sensors offer distinct advantages in imaging applications, including additive manufacturing.
Read our blog post for a more in-depth explanation of how SWIR cameras work.
Understanding Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also called 3D printing or abbreviated to AM, is a process that builds objects layer by layer using computer-controlled systems. Typically, additive manufacturing involves three key stages:
- Design
- Preparation
- Printing
There are numerous advantages to AM, including improved accuracy, lower costs, rapid prototyping, and reduced material waste. However, it also has its challenges, including material limitations and post-processing requirements. In recent years, additive manufacturing has seen emerging trends and advancements, such as improved materials and enhanced complexity of printed objects. But the introduction of SWIR sensors has had a significant impact.
The Role of SWIR Imaging Sensors in Additive Manufacturing
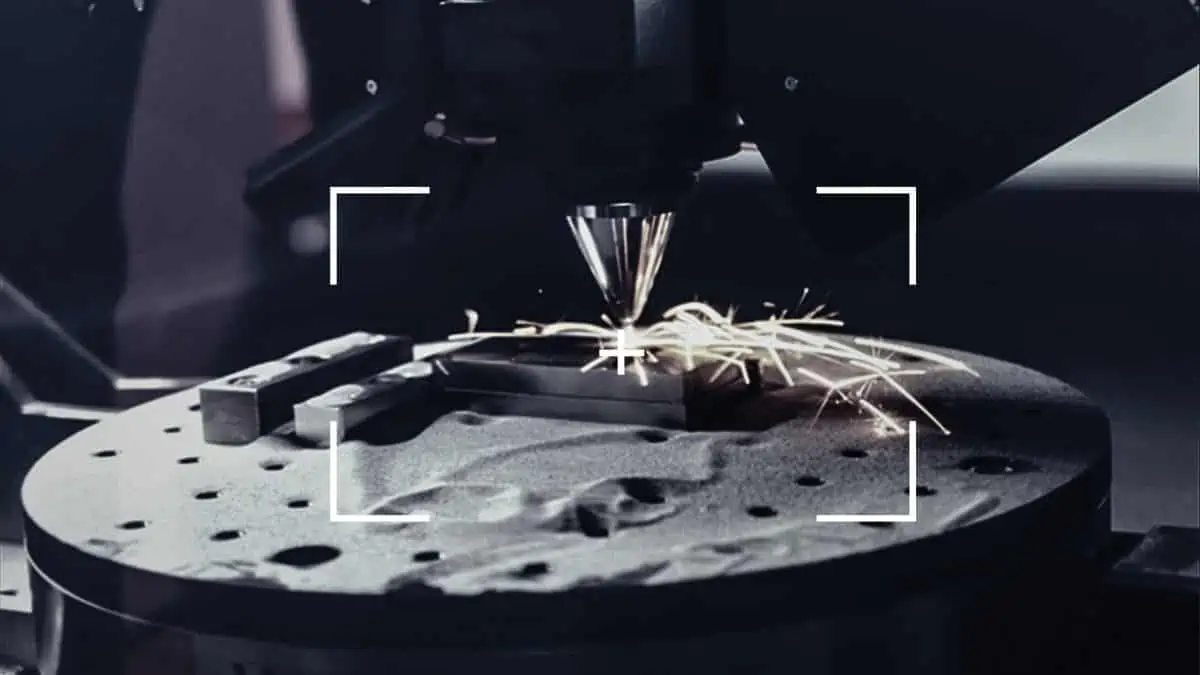
SWIR sensors have found valuable applications in additive manufacturing. They enable defect detection by identifying thermal anomalies invisible to the naked eye or other imaging technologies. Additionally, SWIR imaging aids in boundary detection, ensuring precise printing location and adherence to specifications.
Other crucial applications include the following:
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring air quality, humidity, and particulate matter.
- Quality Control: Inspecting the quality of printed products.
- Real-time Monitoring: Offering vital information about product properties.
- Temperature Control: The environment’s temperature is important, and close monitoring is essential for optimizing printing conditions.
New Imaging Technologies offer State-of-the-Art SWIR Sensors
New Imaging Technologies have invested heavily over the years in all aspects of SWIR technology. This includes camera electronics, photodiode arrays, and software. With in-house manufacturing technologies, we are an integrated source for SWIR sensors and cameras and offer a unique product portfolio for those in additive manufacturing and other industries.
SWIR sensors are used for inspecting parts and monitoring processes, both of which have been difficult to visualize in the past. However, with SWIR cameras that can accurately capture processes such as laser deposition and selective laser melting, operators can clearly monitor fabrication processes. As a result, additive manufacturing methods can be optimized, and overall productivity can be increased.
NIT has developed a range of WiDy SenS cameras fitted with InGaAs sensors, offering unique features suitable for a range of applications. These offer high dynamic range and sensitivity, a comfortable field of view, and a pure-linear mode ideal for monitoring additive manufacturing processes.
SWIR imaging solutions for Additive Manufacturing
To learn more about SWIR sensors and their role in additive manufacturing, contact a member of NIT today.